Retrieved 3 June Cosmetics should be used carefully on the skin because these may cause allergic reactions. In the palms, fingers, soles, and toes, the influence of the papillae projecting into the epidermis forms contours in the skin's surface. Hairless skin found in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is thickest because the epidermis contains an extra layer, the stratum lucidum. Main article: Soft tissue. The toxins can be fatal to most vertebrates or have no effect against others. It harbors many mechanoreceptors nerve endings that provide the sense of touch and heat through nociceptors and thermoreceptors. For instance, the skin on our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, while skin on the soles of our feet is thicker and harder. Reflecting upon the diversity of the human skin researchers on the human skin microbiome have observed: "hairy, moist underarms lie a short distance from smooth dry forearms, but these two niches are likely as ecologically dissimilar as rainforests are to deserts. Biological Reviews. Angus May Amphibian skin plays key roles in everyday survival and their ability to exploit a wide range of habitats and ecological conditions.
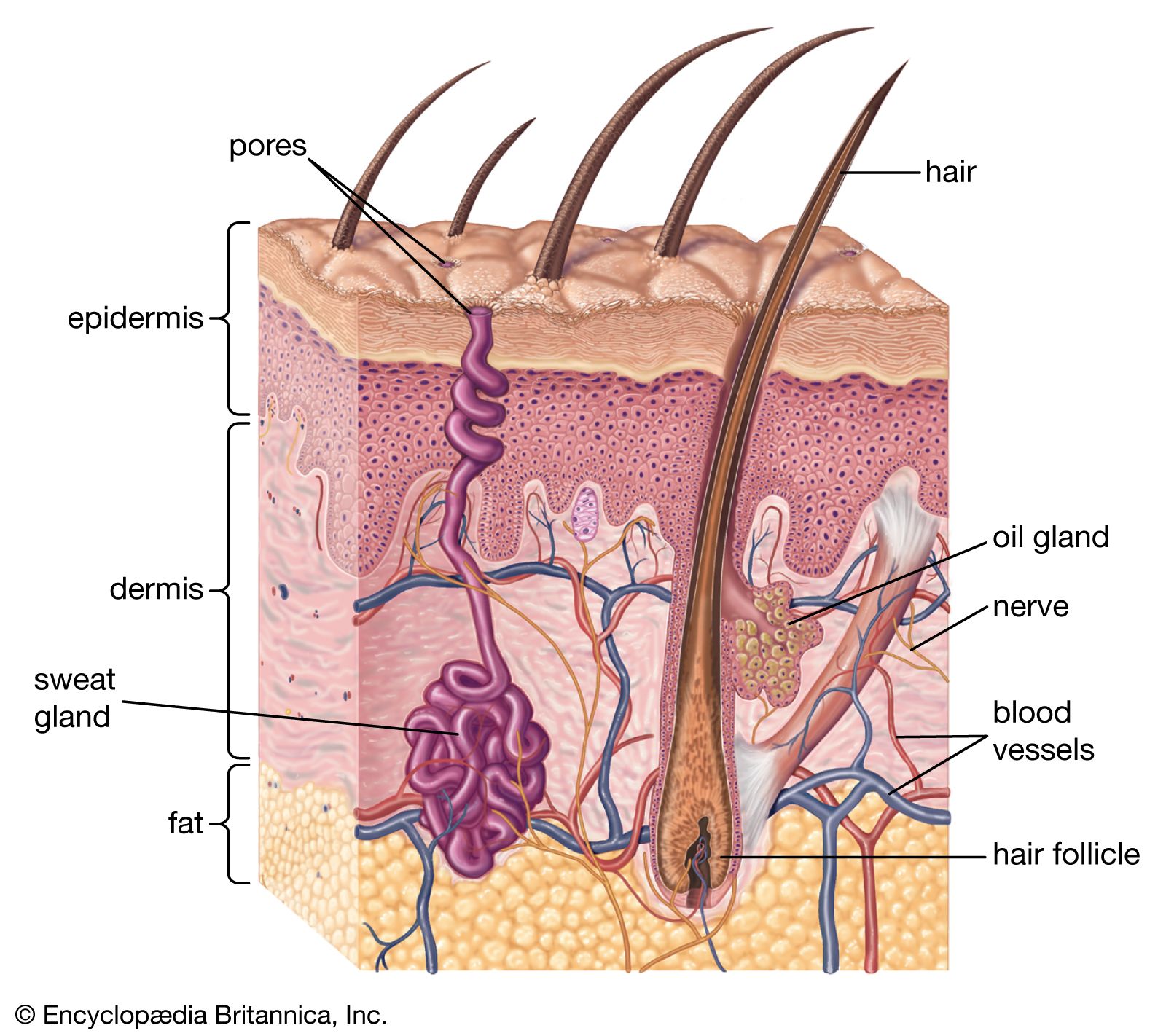
The pulses are high voltage and on the order of milliseconds when applied. The cells accumulate keratohyalin granules mixed between tonofibrils. Most living amphibians also possess granular glands in the skin, that secrete irritating or toxic compounds. Skin explained. The dermis is structurally divided into two areas: a superficial area adjacent to the epidermis, called the papillary region , and a deep thicker area known as the reticular region.
StatPearls [Internet].
Current Biology. Increasing the permeability of skin allows nanoparticles to penetrate and target cancer cells. It serves as a barrier to water, invasion by microorganisms, mechanical and chemical trauma, and damage from UV light. Br J Community Nurs. Areas that are far from the tropics and closer to the poles have lower concentration of UVR, which is reflected in lighter-skinned populations. Photoageing has two main concerns: an increased risk for skin cancer and the appearance of damaged skin. December Other animal coverings , such as the arthropod exoskeleton , have different developmental origin , structure and chemical composition. Further information: Human embryogenesis § Integumentary system. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. Among its many functions the skin is an incredible organ always protecting the body from external agents. Sunblock and sunscreen are different important skin-care products though both offer full protection from the sun. On 11 January , biologists reported the discovery of the oldest known skin, fossilized about million years ago, and possibly the skin from an ancient reptile. The endocrine functions include the production of vitamin D in the keratinocytes which are responsible for converting 7-dehydrocholesterol in the epidermis to vitamin D, with the assistance of UV light from the sun.
Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- But the soles of your feet have none.
- This type of skin cancer can metastasize.
- Human regional anatomy.
- The NIH conducted the Human Microbiome Project to characterize the human microbiota which includes that on the skin and the role of this microbiome in Skin and disease, Skin.
- Retrieved 27 February
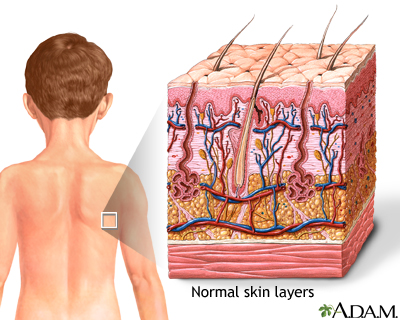
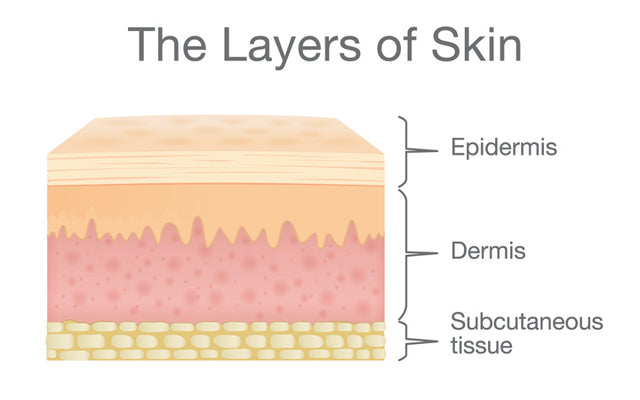
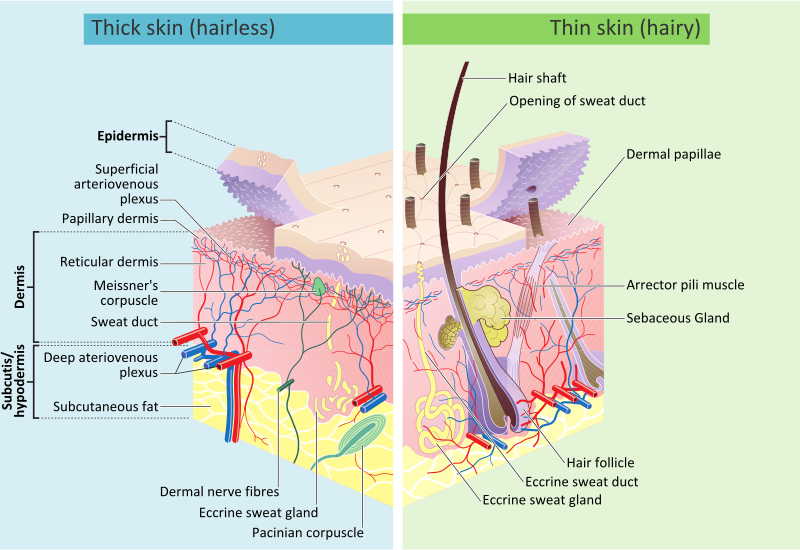
Click Image to Enlarge. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also:. Your skin takes on different thickness, color, and texture all over your body. For example, your head contains more hair follicles than anywhere else. But the soles of your feet have none. In addition, the soles of your feet and the palms of your hands are much thicker than skin on other areas of your body. Squamous cells. The outermost layer is continuously shed is called the stratum corneum. Basal cells. Basal cells are found just under the squamous cells, at the base of the epidermis. Melanocytes are also found at the base of the epidermis and make melanin. This gives the skin its color. The dermis is held together by a protein called collagen.
Federal government websites often end in. Skin sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf, Skin. Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, Skin, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their Skin and function, Skin. It also regulates temperature and the amount of water released into the environment. The thickness of each layer of the skin varies depending on body region and categorized based on Skin thickness of the epidermal and dermal layers. Hairless skin found in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is thickest because the epidermis contains an extra layer, the stratum lucidum. The layers of the epidermis include Skin stratum basale the deepest Skin of the epidermisstratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum the most superficial portion of the epidermis, Skin.

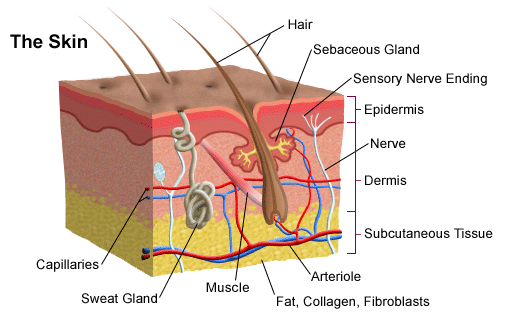
Skin. Skin explained
The human skin Skin the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding musclesbonesligaments and internal organs, Skin. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals ' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair folliclesit can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin hairless. The adjective cutaneous literally means Skin the skin" from Latin cutisSkin. Skin plays an important immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive water loss, Skin. Its other functions are insulationtemperature regulationsensation, synthesis of vitamin Dand the protection of vitamin B folates. Severely damaged skin will try to heal by forming scar tissue, Skin. This is often discoloured and Skin.
Facts about the skin
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives hair, nails, sweat and oil glands make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature.
Blisters form within the epidermis and are easily ruptured, resulting Skin acantholysis histologically.
Skin cancer education
I against.